2 月 . 15, 2025 12:43 Back to list
deep well submersible pump
Submersible pumps have emerged as a cornerstone in various industries owing to their efficiency and high performance in moving fluids from one location to another. These pumps function by being entirely submerged in the liquid they are meant to pump, which inherently makes them highly efficient. Here’s a comprehensive look at the pivotal features and applications of submersible pumps, specifically focusing on models that involve 4 submersible pump systems.
Real-world applications and experiences show that maintaining submersible pumps is straightforward, though routine inspections are crucial to ensure optimal performance. Regular checks on seals, bearings, and motor function can preemptively address issues before they lead to significant downtime—reflecting the pump’s reliability and its pivotal role in ongoing operations across sectors. Submersibles, particularly those categorized under 4 submersible pump configurations, afford a level of dependability and performance that are highly regarded in industry circles. Their versatility in tackling diverse challenges while maintaining water and energy efficiency establishes their authority in any fluid management system. Trust in submersible pump technology is bolstered by industry standards and compliance with regulations that promote environmental responsibility and energy conservation. Users and professionals alike not only gauge these pumps' performance metrics but also place significant emphasis on their compliance with global environmental norms, reflecting trustworthiness and reliability. In conclusion, the 4 submersible pump systems stand as a testament to engineering ingenuity, offering seamless performance across various applications. The combination of efficiency, reliability, and adaptability makes them a top choice, helping industries across the globe manage their water and fluid requirements with confidence and precision.
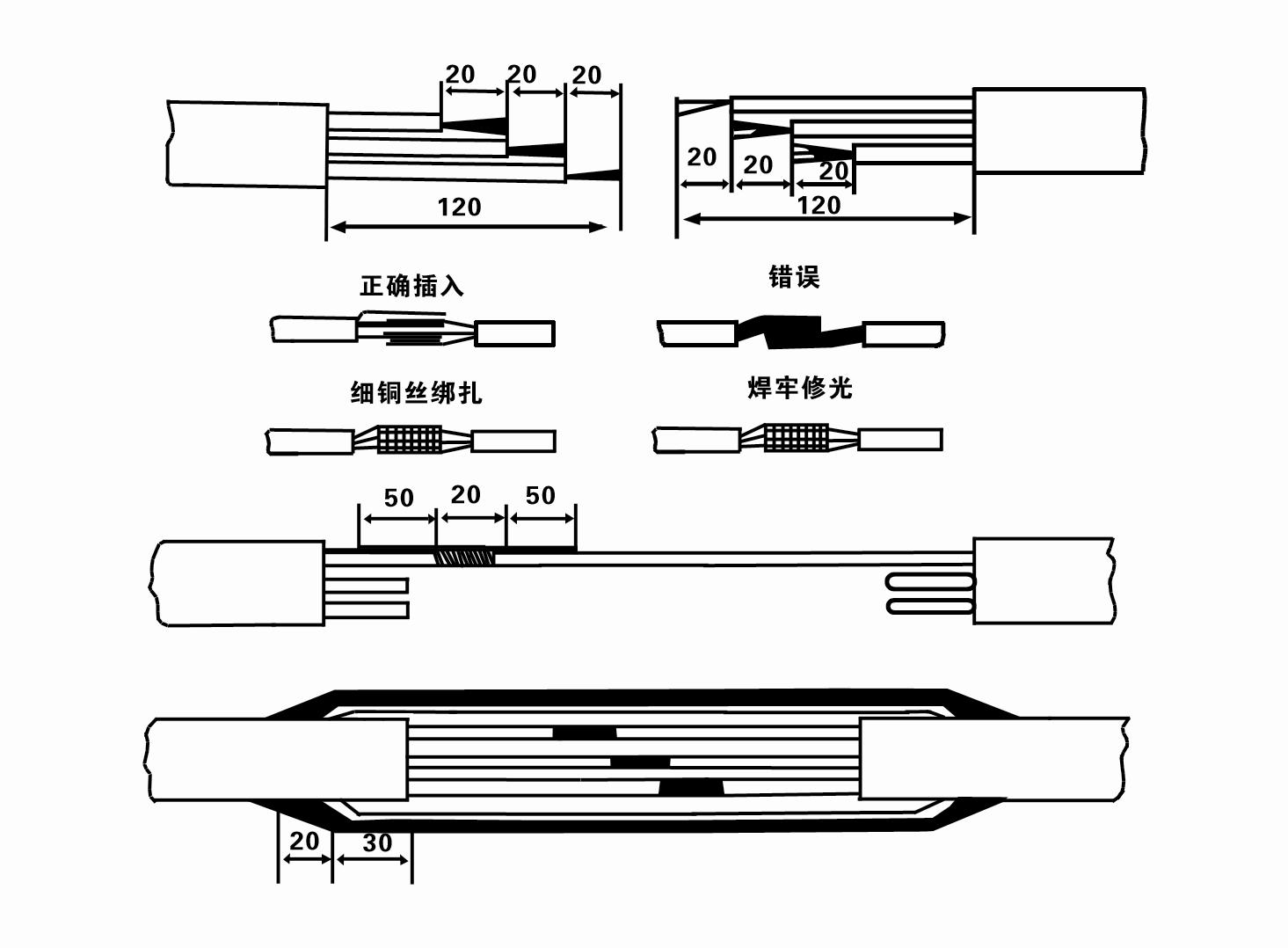
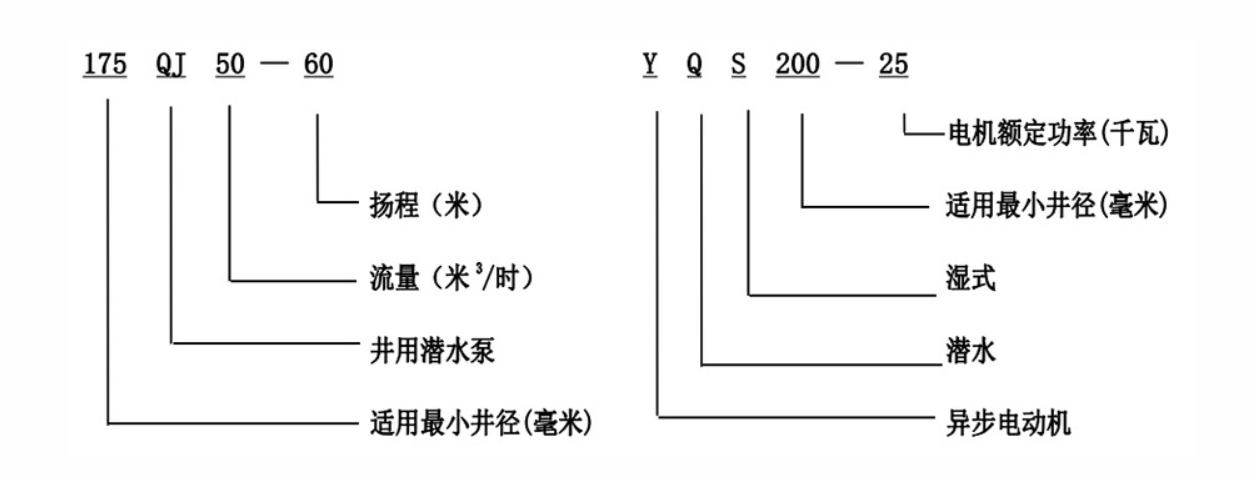
Real-world applications and experiences show that maintaining submersible pumps is straightforward, though routine inspections are crucial to ensure optimal performance. Regular checks on seals, bearings, and motor function can preemptively address issues before they lead to significant downtime—reflecting the pump’s reliability and its pivotal role in ongoing operations across sectors. Submersibles, particularly those categorized under 4 submersible pump configurations, afford a level of dependability and performance that are highly regarded in industry circles. Their versatility in tackling diverse challenges while maintaining water and energy efficiency establishes their authority in any fluid management system. Trust in submersible pump technology is bolstered by industry standards and compliance with regulations that promote environmental responsibility and energy conservation. Users and professionals alike not only gauge these pumps' performance metrics but also place significant emphasis on their compliance with global environmental norms, reflecting trustworthiness and reliability. In conclusion, the 4 submersible pump systems stand as a testament to engineering ingenuity, offering seamless performance across various applications. The combination of efficiency, reliability, and adaptability makes them a top choice, helping industries across the globe manage their water and fluid requirements with confidence and precision.
Latest news
-
Your Guide to Deep Well Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Why Choose a Stainless Steel Deep Well Pump?
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Understanding Water-Filled Submersible Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Understanding SS Submersible Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Reliable Submersible Well Pumps for Your Water Supply Needs
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Choosing the Right Submersible Pump for Your Water Management Needs
NewsOct.31,2024
-
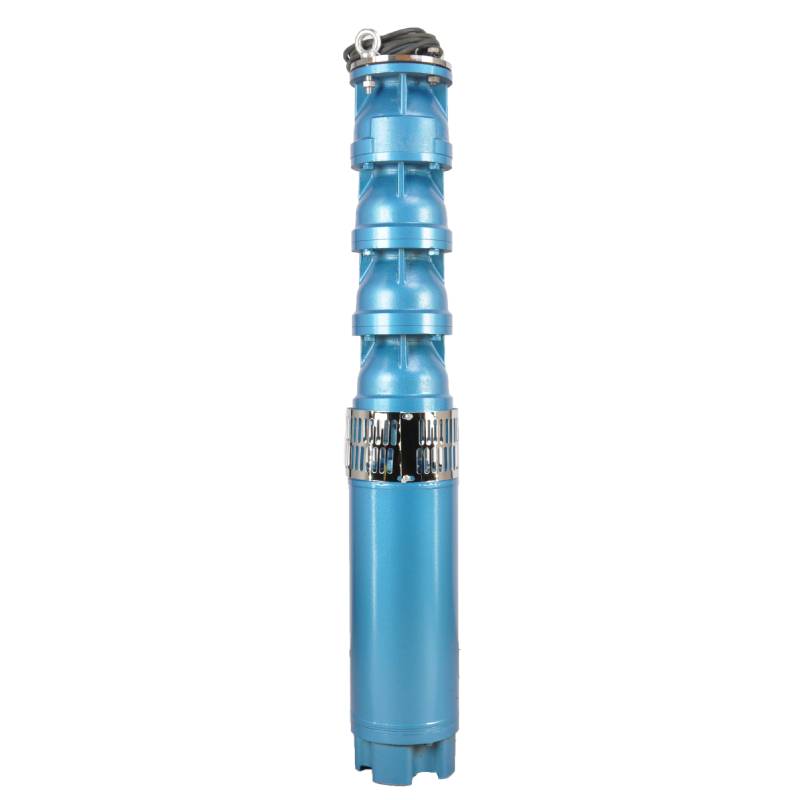 Understanding Water-Filled Submersible PumpsWhen it comes to selecting the right pump for your water management needs, understanding the different types available is crucial.Detail
Understanding Water-Filled Submersible PumpsWhen it comes to selecting the right pump for your water management needs, understanding the different types available is crucial.Detail -
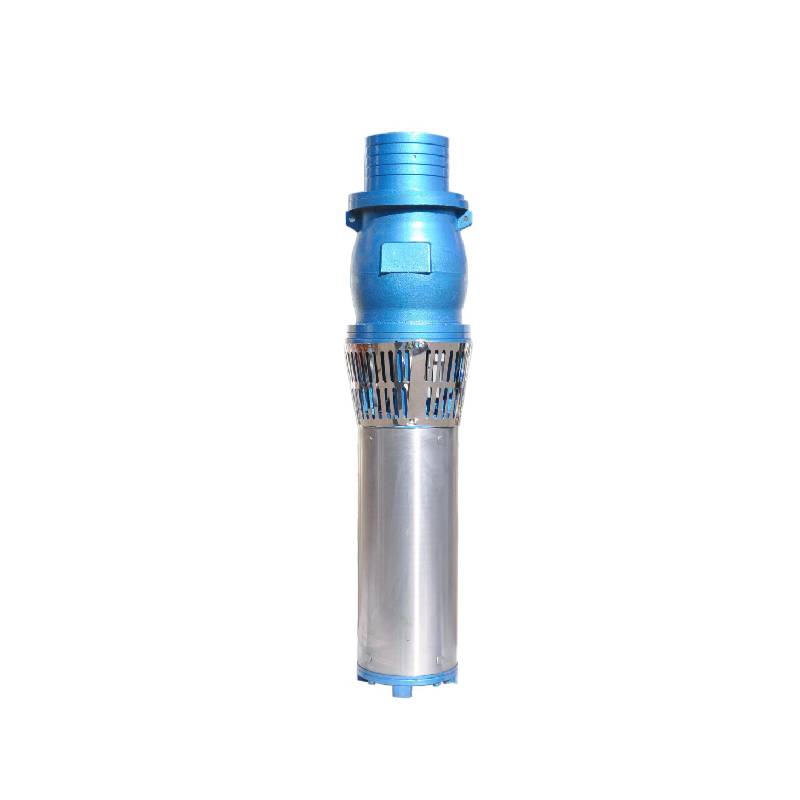 Guide to Installing a Deep Well Submersible PumpWhen dealing with deep wells, a deep well submersible pump is often the most effective solution for extracting water from significant depths.Detail
Guide to Installing a Deep Well Submersible PumpWhen dealing with deep wells, a deep well submersible pump is often the most effective solution for extracting water from significant depths.Detail -
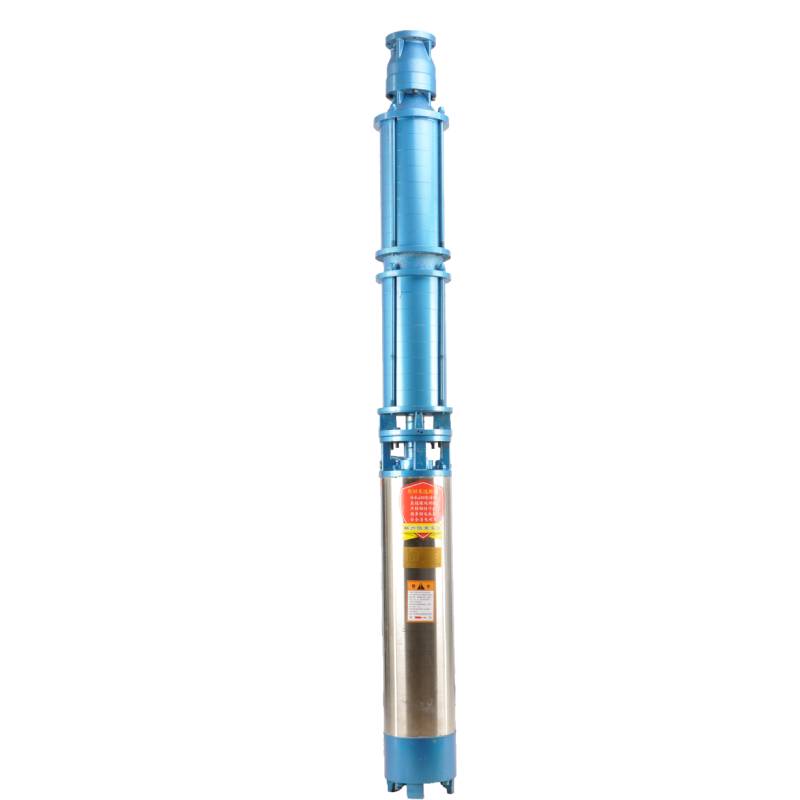 Finding the Right Submersible PumpWhen seeking an efficient solution for pumping water from deep wells, sumps, or other applications, the submersible pump is a leading choice.Detail
Finding the Right Submersible PumpWhen seeking an efficient solution for pumping water from deep wells, sumps, or other applications, the submersible pump is a leading choice.Detail
