12 月 . 03, 2024 16:27 Back to list
Guide to Fixing a Deep Well Submersible Pump Efficiently and Effectively
How to Repair a Deep Well Submersible Pump
A deep well submersible pump is an essential component in many water systems, designed to pump water from deep underground sources to the surface. Over time, these pumps can encounter issues that necessitate repairs to restore their functionality. Understanding how to troubleshoot and repair a submersible pump can save both time and money. Below is a guide to help you successfully navigate the repair process.
Step 1 Safety First
Before starting any repair work, ensure your safety. Disconnect the pump from the power source to avoid accidental electrocution. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as gloves and safety goggles. If the pump is located in a well, take precautions to ensure your safety around the well and any equipment you may use.
Step 2 Identify the Problem
Common issues with submersible pumps include noise, excessive vibration, low water output, or the pump not turning on at all. Listen closely to your pump when it's operational; unusual sounds can indicate problems. Additionally, check for visible leaks or physical damage to the pump.
Step 3 Remove the Pump
To repair the submersible pump, it must be removed from the well. This typically involves using a pipe wrench to unthread the pump from the discharge pipe. Carefully pull the pump out of the well casing, ensuring not to damage the electric wires or piping. Once removed, inspect the pump and components for any visible signs of wear or damage.
Step 4 Inspect Components
Once the pump is out of the well, begin a thorough inspection of its components, including
- Motor Check for signs of overheating, wear, or corrosion. - Impeller Inspect the impeller for damage or debris stuck in the blades, which can impede performance. - Suction Strainer Ensure the strainer is clear and free of blockages that could restrict water flow. - Seals and Bearings Look for signs of wear in the seals and bearings, as these can lead to leaks and reduced efficiency.
Step 5 Clean the Components
how to repair a deep well submersible pump
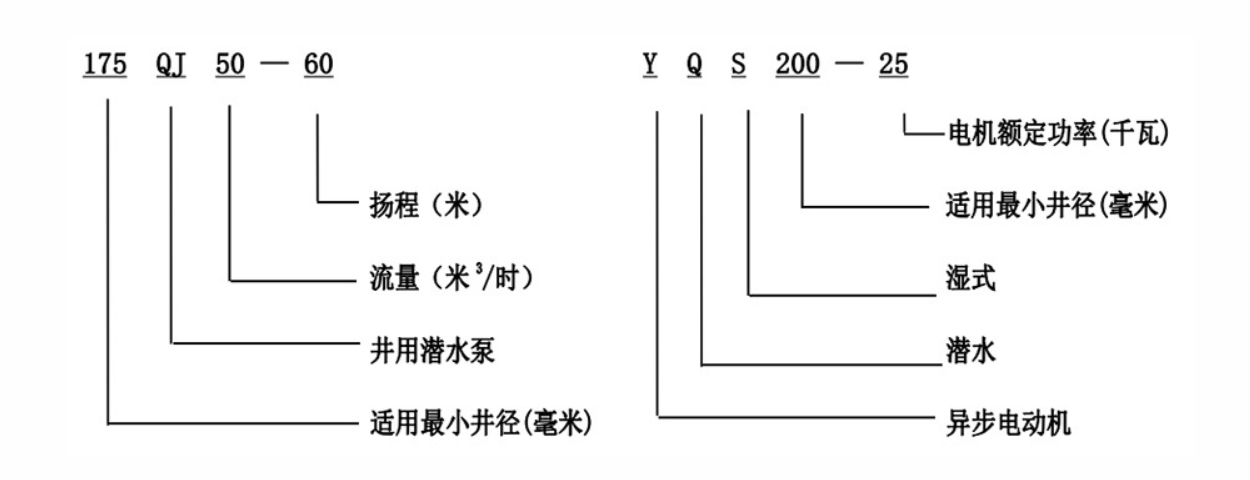
If you notice debris or sediment buildup, clean the components using water and a mild detergent. Use a toothbrush or a soft brush to remove dirt from hard-to-reach areas. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasives that could damage the components.
Step 6 Repair or Replace Damaged Parts
If you find damaged components during your inspection, you have a choice repair or replace them. For small abrasions or minor issues, it may be possible to apply sealant or grease. However, for severely damaged parts, it’s generally best to replace them. Most pump manufacturers provide replacement parts that you can purchase.
Step 7 Reassemble the Pump
After making repairs or replacements, reassemble the pump carefully. Ensure that all screws, bolts, and fittings are secured tightly to prevent leaks. Reconnect the electrical wiring, taking care to match the connections correctly. If you're unsure of the wiring diagram, consult the user manual or seek professional assistance.
Step 8 Test the Pump
Once the pump is reassembled and back in the well, it's time to test it. Turn the power back on and monitor the pump for any unusual noises or vibrations. Check the water output to ensure it's functioning as expected. If the pump operates smoothly and efficiently, you have successfully completed the repair.
Step 9 Preventive Maintenance
To avoid future repairs, establish a routine maintenance schedule. Periodically check the pump for signs of wear or damage, clean the components regularly, and ensure the electrical connections remain secure. By taking preventative measures, you can prolong the lifespan of your deep well submersible pump and ensure reliable water supply year-round.
Conclusion
Repairing a deep well submersible pump can be a manageable task if approached carefully and methodically. By following these steps, you can troubleshoot issues, perform necessary repairs, and maintain the efficiency of your water system. Always prioritize safety and consult a professional if you encounter complex problems beyond your expertise.
-
Your Guide to Deep Well Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Why Choose a Stainless Steel Deep Well Pump?
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Understanding Water-Filled Submersible Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Understanding SS Submersible Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Reliable Submersible Well Pumps for Your Water Supply Needs
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Choosing the Right Submersible Pump for Your Water Management Needs
NewsOct.31,2024
-
 Understanding Water-Filled Submersible PumpsWhen it comes to selecting the right pump for your water management needs, understanding the different types available is crucial.Detail
Understanding Water-Filled Submersible PumpsWhen it comes to selecting the right pump for your water management needs, understanding the different types available is crucial.Detail -
 Guide to Installing a Deep Well Submersible PumpWhen dealing with deep wells, a deep well submersible pump is often the most effective solution for extracting water from significant depths.Detail
Guide to Installing a Deep Well Submersible PumpWhen dealing with deep wells, a deep well submersible pump is often the most effective solution for extracting water from significant depths.Detail -
 Finding the Right Submersible PumpWhen seeking an efficient solution for pumping water from deep wells, sumps, or other applications, the submersible pump is a leading choice.Detail
Finding the Right Submersible PumpWhen seeking an efficient solution for pumping water from deep wells, sumps, or other applications, the submersible pump is a leading choice.Detail
