3 月 . 07, 2025 01:54 Back to list
how to test a submersible pump with a multimeter
Testing a submersible pump with a multimeter is a crucial skill for anyone involved in pump maintenance or repair work. Submersible pumps, primarily used in water supply, sewage treatment, and drainage systems, are vital components in many industrial and residential applications. As an expert, understanding how to efficiently and safely test these pumps ensures reliable operation and longevity, extending their lifespan and maintaining optimal performance.
Analyzing the continuity of the motor winding is another critical step. With the multimeter set to continuity mode, probe the terminals of the windings. A continuous tone indicates good continuity, while an absence signifies a break in the winding circuit, suggesting damage that could prevent the pump from operating correctly. Interpreting these test results requires expertise. Consistent readings and high insulation resistance typically suggest that the motor is in good working condition. However, irregularities such as low insulation resistance or absent continuity should be addressed immediately by a professional. Additionally, visual inspection of the pump components, including the power cables, seals, and casings, can offer insights into potential physical damage or wear and tear that may not be detected by electrical testing alone. Regular inspections ensure the mechanical integrity of the pump, vital for preventing breakdowns. In sum, understanding and executing these diagnostic steps not only showcases technical expertise but also reinforces reliability and trustworthiness in pump maintenance. Maintaining thorough documentation of each test and continually updating your knowledge with the latest industry practices enhances the quality and authenticity of your work. Employing regular testing not only extends the life of the submersible pump but also mitigates risks associated with faulty equipment, ensuring safe and efficient operations in all applications. By adhering to these guidelines, you support not just the functionality of the pumps but also the safety and satisfaction of those relying on them.

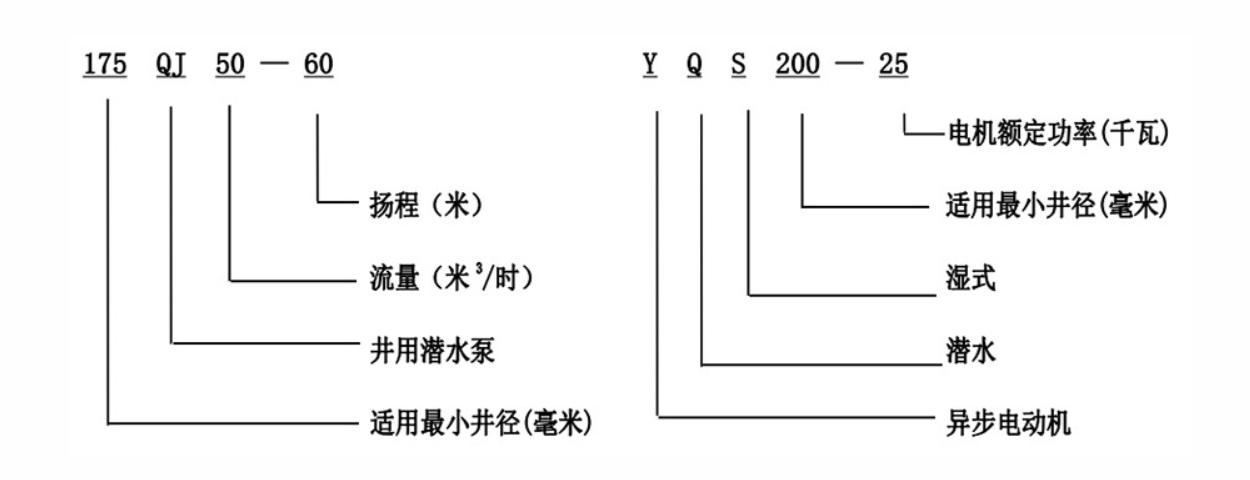
Analyzing the continuity of the motor winding is another critical step. With the multimeter set to continuity mode, probe the terminals of the windings. A continuous tone indicates good continuity, while an absence signifies a break in the winding circuit, suggesting damage that could prevent the pump from operating correctly. Interpreting these test results requires expertise. Consistent readings and high insulation resistance typically suggest that the motor is in good working condition. However, irregularities such as low insulation resistance or absent continuity should be addressed immediately by a professional. Additionally, visual inspection of the pump components, including the power cables, seals, and casings, can offer insights into potential physical damage or wear and tear that may not be detected by electrical testing alone. Regular inspections ensure the mechanical integrity of the pump, vital for preventing breakdowns. In sum, understanding and executing these diagnostic steps not only showcases technical expertise but also reinforces reliability and trustworthiness in pump maintenance. Maintaining thorough documentation of each test and continually updating your knowledge with the latest industry practices enhances the quality and authenticity of your work. Employing regular testing not only extends the life of the submersible pump but also mitigates risks associated with faulty equipment, ensuring safe and efficient operations in all applications. By adhering to these guidelines, you support not just the functionality of the pumps but also the safety and satisfaction of those relying on them.
Latest news
-
Your Guide to Deep Well Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Why Choose a Stainless Steel Deep Well Pump?
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Understanding Water-Filled Submersible Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Understanding SS Submersible Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Reliable Submersible Well Pumps for Your Water Supply Needs
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Choosing the Right Submersible Pump for Your Water Management Needs
NewsOct.31,2024
-
 Understanding Water-Filled Submersible PumpsWhen it comes to selecting the right pump for your water management needs, understanding the different types available is crucial.Detail
Understanding Water-Filled Submersible PumpsWhen it comes to selecting the right pump for your water management needs, understanding the different types available is crucial.Detail -
 Guide to Installing a Deep Well Submersible PumpWhen dealing with deep wells, a deep well submersible pump is often the most effective solution for extracting water from significant depths.Detail
Guide to Installing a Deep Well Submersible PumpWhen dealing with deep wells, a deep well submersible pump is often the most effective solution for extracting water from significant depths.Detail -
 Finding the Right Submersible PumpWhen seeking an efficient solution for pumping water from deep wells, sumps, or other applications, the submersible pump is a leading choice.Detail
Finding the Right Submersible PumpWhen seeking an efficient solution for pumping water from deep wells, sumps, or other applications, the submersible pump is a leading choice.Detail
