2 月 . 18, 2025 01:14 Back to list
300QJR Deep Well Submersible Pump
Submersible water well pumps are essential tools for accessing groundwater, but ensuring their integrity and functionality requires a systematic approach to testing. This guide combines professional expertise and authoritative advice to ensure your pump operates at optimal levels.
Vibration Analysis Excessive vibration can signal mechanical issues that may not be visible during inspection. Use a vibration analyzer to assess the intensity and frequency of vibrations while the pump is operating. Consistent vibration patterns are normal; however, spikes or irregularities could indicate imbalance or damage to internal components. Endurance Testing If testing is feasible, conduct an endurance test by operating the pump continuously for several hours. This will not only confirm the reliability of the pump under sustained use but also highlight any issues that might arise under typical operating conditions. During this time, continuously monitor temperature, pressure, and flow rate. Documentation and Reporting Document all testing procedures and results meticulously. This creates a reference for future maintenance schedules and repairs. Keeping comprehensive records of initial settings, tested parameters, and any deviations from normative values assists in diagnosing recurrent problems. Consultation with Experts Collaboration with pump specialists and manufacturers offers additional insights that may not be apparent through basic testing. Such experts can provide a nuanced understanding of specific pump models and potential troubleshooting methods. By adhering to these carefully structured testing stages, and combining personal expertise with industry-standard practices, you ensure not only the pump’s efficiency but also extend its operational life. This systematic approach not only enhances the credibility and authority of your maintenance practices but establishes trustworthiness in your methods, instilling confidence in stakeholders who rely on the consistency of groundwater delivery solutions.
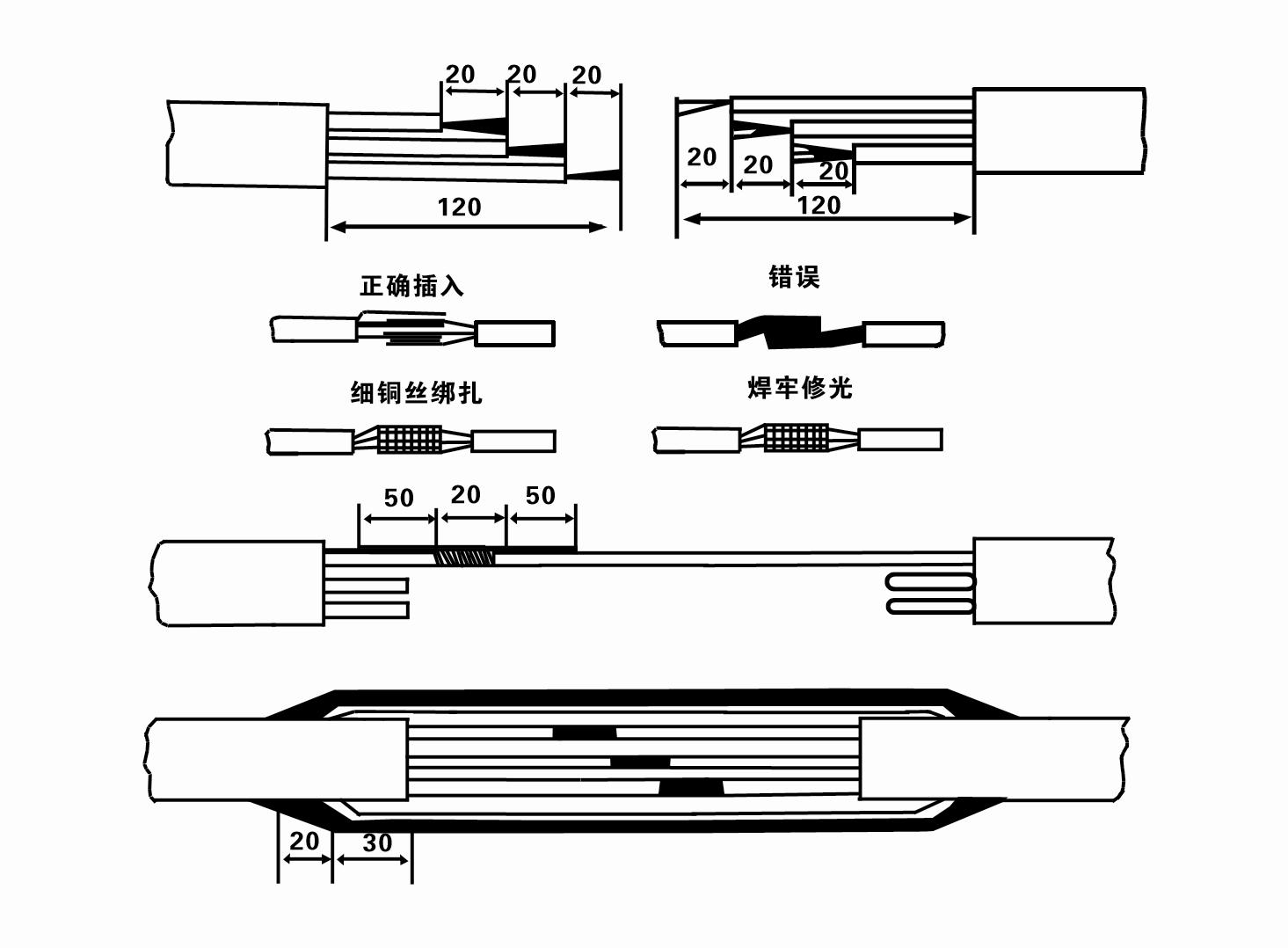

Vibration Analysis Excessive vibration can signal mechanical issues that may not be visible during inspection. Use a vibration analyzer to assess the intensity and frequency of vibrations while the pump is operating. Consistent vibration patterns are normal; however, spikes or irregularities could indicate imbalance or damage to internal components. Endurance Testing If testing is feasible, conduct an endurance test by operating the pump continuously for several hours. This will not only confirm the reliability of the pump under sustained use but also highlight any issues that might arise under typical operating conditions. During this time, continuously monitor temperature, pressure, and flow rate. Documentation and Reporting Document all testing procedures and results meticulously. This creates a reference for future maintenance schedules and repairs. Keeping comprehensive records of initial settings, tested parameters, and any deviations from normative values assists in diagnosing recurrent problems. Consultation with Experts Collaboration with pump specialists and manufacturers offers additional insights that may not be apparent through basic testing. Such experts can provide a nuanced understanding of specific pump models and potential troubleshooting methods. By adhering to these carefully structured testing stages, and combining personal expertise with industry-standard practices, you ensure not only the pump’s efficiency but also extend its operational life. This systematic approach not only enhances the credibility and authority of your maintenance practices but establishes trustworthiness in your methods, instilling confidence in stakeholders who rely on the consistency of groundwater delivery solutions.
Latest news
-
Your Guide to Deep Well Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Why Choose a Stainless Steel Deep Well Pump?
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Understanding Water-Filled Submersible Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Understanding SS Submersible Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Reliable Submersible Well Pumps for Your Water Supply Needs
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Choosing the Right Submersible Pump for Your Water Management Needs
NewsOct.31,2024
-
 Understanding Water-Filled Submersible PumpsWhen it comes to selecting the right pump for your water management needs, understanding the different types available is crucial.Detail
Understanding Water-Filled Submersible PumpsWhen it comes to selecting the right pump for your water management needs, understanding the different types available is crucial.Detail -
 Guide to Installing a Deep Well Submersible PumpWhen dealing with deep wells, a deep well submersible pump is often the most effective solution for extracting water from significant depths.Detail
Guide to Installing a Deep Well Submersible PumpWhen dealing with deep wells, a deep well submersible pump is often the most effective solution for extracting water from significant depths.Detail -
 Finding the Right Submersible PumpWhen seeking an efficient solution for pumping water from deep wells, sumps, or other applications, the submersible pump is a leading choice.Detail
Finding the Right Submersible PumpWhen seeking an efficient solution for pumping water from deep wells, sumps, or other applications, the submersible pump is a leading choice.Detail
