2 月 . 16, 2025 11:38 Back to list
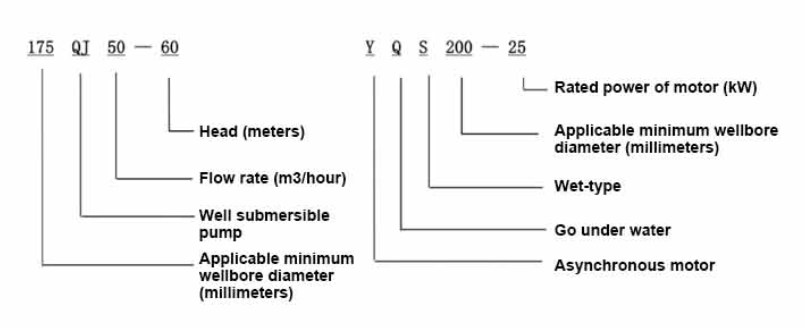
175QJ Deep Well Submersible Pump
Testing a submersible well pump is a crucial process for ensuring that water systems are functioning optimally and reliably. This involves precise steps and consideration of several factors including electrical safety, mechanical integrity, and water output efficiency. Understanding how to effectively test a submersible well pump not only prolongs the life of the pump but also ensures consistent water supply.
Another vital aspect is testing the check valve. This component prevents water from flowing back into the well once pumped to the surface. A faulty check valve can cause the pump to work inefficiently, leading to premature wear. Listen for water hammer noises that suggest a malfunctioning valve, or observe water pressure fluctuations when the pump starts and stops, which might indicate valve failure. Assess the overall water quality as part of the testing process. Poor water quality can disrupt pump operation and contribute to longer-term damage. Elements like sand, silt, and other particulates can be particularly damaging, eroding pump components and obstructing flow paths. Conducting a particle count and chemical analysis of the water can provide early warnings of potential issues. For a comprehensive evaluation of pump health, consider the installation of a pump monitor. These devices give real-time data on pump performance, measuring metrics such as current consumption, motor temperature, and operating hours. Advanced models can alert users to anomalies that suggest declining efficiency. Finally, document all observed data and results from the tests. This historical data forms a critical database for future maintenance and operational adjustments. Should professional intervention be necessary, these records will be invaluable for technicians addressing more complex issues. Testing a submersible well pump accurately requires attention to detail and adherence to defined protocols. Although many homeowners can conduct preliminary tests, engaging a qualified technician ensures detailed analysis and resolution of intricate issues. Regular testing is vital to maintain the functionality and longevity of the pump, safeguarding against unexpected disruptions in water supply. The tasks demand a combination of electrical skills, mechanical understanding, and detailed observation—essentials in cementing the reliable performance of submersible well pumps.

Another vital aspect is testing the check valve. This component prevents water from flowing back into the well once pumped to the surface. A faulty check valve can cause the pump to work inefficiently, leading to premature wear. Listen for water hammer noises that suggest a malfunctioning valve, or observe water pressure fluctuations when the pump starts and stops, which might indicate valve failure. Assess the overall water quality as part of the testing process. Poor water quality can disrupt pump operation and contribute to longer-term damage. Elements like sand, silt, and other particulates can be particularly damaging, eroding pump components and obstructing flow paths. Conducting a particle count and chemical analysis of the water can provide early warnings of potential issues. For a comprehensive evaluation of pump health, consider the installation of a pump monitor. These devices give real-time data on pump performance, measuring metrics such as current consumption, motor temperature, and operating hours. Advanced models can alert users to anomalies that suggest declining efficiency. Finally, document all observed data and results from the tests. This historical data forms a critical database for future maintenance and operational adjustments. Should professional intervention be necessary, these records will be invaluable for technicians addressing more complex issues. Testing a submersible well pump accurately requires attention to detail and adherence to defined protocols. Although many homeowners can conduct preliminary tests, engaging a qualified technician ensures detailed analysis and resolution of intricate issues. Regular testing is vital to maintain the functionality and longevity of the pump, safeguarding against unexpected disruptions in water supply. The tasks demand a combination of electrical skills, mechanical understanding, and detailed observation—essentials in cementing the reliable performance of submersible well pumps.
Latest news
-
Your Guide to Deep Well Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Why Choose a Stainless Steel Deep Well Pump?
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Understanding Water-Filled Submersible Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Understanding SS Submersible Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Reliable Submersible Well Pumps for Your Water Supply Needs
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Choosing the Right Submersible Pump for Your Water Management Needs
NewsOct.31,2024
-
 Understanding Water-Filled Submersible PumpsWhen it comes to selecting the right pump for your water management needs, understanding the different types available is crucial.Detail
Understanding Water-Filled Submersible PumpsWhen it comes to selecting the right pump for your water management needs, understanding the different types available is crucial.Detail -
 Guide to Installing a Deep Well Submersible PumpWhen dealing with deep wells, a deep well submersible pump is often the most effective solution for extracting water from significant depths.Detail
Guide to Installing a Deep Well Submersible PumpWhen dealing with deep wells, a deep well submersible pump is often the most effective solution for extracting water from significant depths.Detail -
 Finding the Right Submersible PumpWhen seeking an efficient solution for pumping water from deep wells, sumps, or other applications, the submersible pump is a leading choice.Detail
Finding the Right Submersible PumpWhen seeking an efficient solution for pumping water from deep wells, sumps, or other applications, the submersible pump is a leading choice.Detail
