9 月 . 25, 2024 09:28 Back to list
Guidelines for Conducting Tests on Submersible Well Pumps Effectively and Safely
How to Test a Submersible Well Pump
Testing a submersible well pump is essential to ensure its efficiency and longevity. Whether you're troubleshooting issues or conducting routine maintenance, performing a proper test can help identify potential problems and optimize the pump's performance. Below is a comprehensive guide on how to test a submersible well pump effectively.
1. Safety First
Before starting the testing process, prioritize safety. Ensure that the power supply to the pump is turned off to prevent any electrical hazards. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as gloves and safety goggles, to safeguard yourself from potential injuries.
2. Inspect the Components
Begin by visually inspecting the pump and its associated components. Check for any signs of physical damage, corrosion, or wear on the pump casing, discharge pipes, and electrical connections. Make sure that all fittings are tight, and there are no visible leaks.
3. Measure Submergence Depth
Measure the depth of the water in the well. This helps ensure that the pump is submerged adequately. A pump that is not fully submerged may not operate efficiently and can lead to damage over time. The recommended submergence depth varies based on the pump model, so consult the manufacturer’s specifications.
how to test a submersible well pump
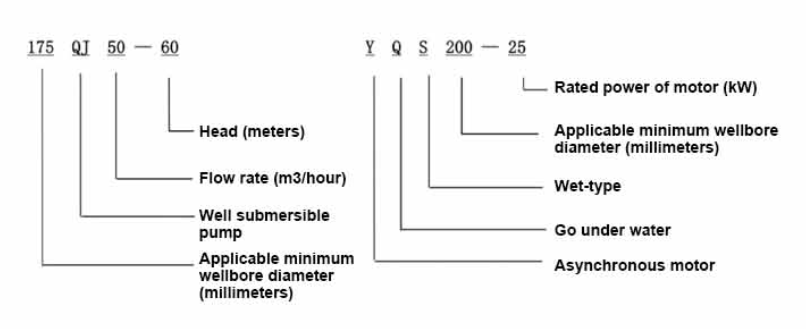
Using a multimeter, check the voltage at the control box and the amperage drawn by the pump during operation. Compare these readings with the pump specifications. Low voltage can hinder performance, while excessive amperage may indicate an overload issue or a malfunction.
5. Flow Rate Test
Conduct a flow rate test to determine the pump’s performance. You can do this by measuring the time it takes to fill a known volume of water, such as a tank or bucket. Record the flow rate in gallons per minute (GPM) and compare it to the manufacturer's specifications. If the flow rate is below the acceptable level, there might be issues like clogs or wear in the pump components.
6. Pressure Testing
If your pump is connected to a pressure tank, check the pressure settings. With the pump running, observe the pressure gauge. The readings should fluctuate within a specified range, typically between 40 to 60 PSI. If the pressure does not reach this range, the pump may be malfunctioning.
7. Listen for Unusual Noises
During operation, pay attention to unusual sounds, such as grinding or rattling. These noises may indicate mechanical wear or failure within the pump. If you notice any irregular sounds, it may be time to consult a professional for further assessment.
Conclusion
Testing a submersible well pump is crucial for maintaining a reliable water supply. By following these steps, you can identify potential issues early and perform necessary maintenance, ensuring that your pump operates efficiently for years to come. Regular testing not only saves money but also prolongs the lifespan of your well system.
-
Your Guide to Deep Well Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Why Choose a Stainless Steel Deep Well Pump?
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Understanding Water-Filled Submersible Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Understanding SS Submersible Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Reliable Submersible Well Pumps for Your Water Supply Needs
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Choosing the Right Submersible Pump for Your Water Management Needs
NewsOct.31,2024
-
 Understanding Water-Filled Submersible PumpsWhen it comes to selecting the right pump for your water management needs, understanding the different types available is crucial.Detail
Understanding Water-Filled Submersible PumpsWhen it comes to selecting the right pump for your water management needs, understanding the different types available is crucial.Detail -
 Guide to Installing a Deep Well Submersible PumpWhen dealing with deep wells, a deep well submersible pump is often the most effective solution for extracting water from significant depths.Detail
Guide to Installing a Deep Well Submersible PumpWhen dealing with deep wells, a deep well submersible pump is often the most effective solution for extracting water from significant depths.Detail -
 Finding the Right Submersible PumpWhen seeking an efficient solution for pumping water from deep wells, sumps, or other applications, the submersible pump is a leading choice.Detail
Finding the Right Submersible PumpWhen seeking an efficient solution for pumping water from deep wells, sumps, or other applications, the submersible pump is a leading choice.Detail
