11 月 . 01, 2024 20:17 Back to list
Exploring the Efficiency and Applications of Submersible Pump Technology in Various Industries
Exploring Submersible Pumps An Overview
Submersible pumps are an essential component in various industries and applications, particularly for water management and fluid transfer. These pumps are designed to operate while submerged in the fluid they are pumping, which enhances their efficiency and safety. This article will delve into the working principle, types, applications, and advantages of submersible pumps.
Working Principle
A submersible pump consists of a motor and a pump body, both of which are submerged in the fluid. The pump operates by using a centrifugal or positive displacement design to draw fluid into the impeller and push it to the surface through a discharge pipe. When the pump is submerged, it is protected from the outside environmental conditions, and its motor is sealed to prevent damage from the fluid. This design allows the pump to handle various types of liquids, including clean water, wastewater, and even chemicals, depending on the materials used.
Types of Submersible Pumps
There are several types of submersible pumps, each suited for specific applications
1. Centrifugal Submersible Pumps These pumps utilize a rotating impeller to create centrifugal force that moves fluid. They are commonly used for pumping clean water in residential and agricultural applications.
2. Positive Displacement Submersible Pumps These pumps move fluid by trapping a fixed amount of fluid and forcing it into the discharge. They are ideal for pumping viscous fluids or liquids with high solids content, such as sludge.
3. Sump Pumps Designed to remove water from basements or low-lying areas, sump pumps are typically used in residential settings to prevent flooding.
4. Effluent Pumps These pumps are used to move wastewater from a septic tank or a holding tank to a drain field or treatment facility.
Applications
Submersible pumps find applications in various fields
submersible pumps
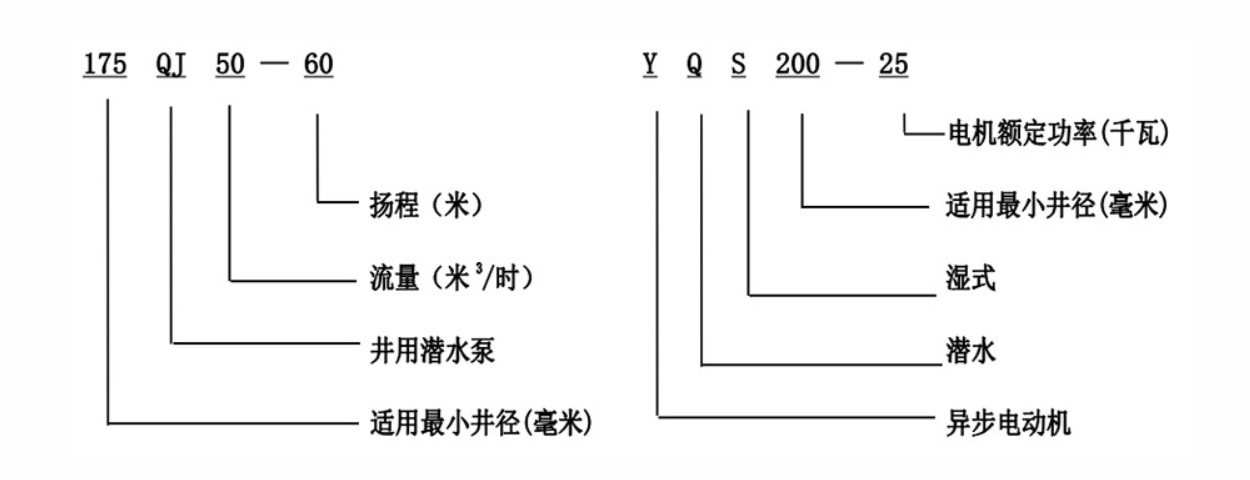
- Water Supply They are widely utilized in residential water systems, boreholes, and agricultural irrigation to draw groundwater.
- Wastewater Management In municipal settings, submersible pumps are crucial for managing sewage and wastewater treatment processes
.- Oil and Gas Submersible pumps are used to extract fluids from deep wells, facilitating the production of oil and gas.
- Industrial Use Many industries rely on these pumps to handle fluids in manufacturing processes, chemical handling, and cooling systems.
Advantages
The advantages of submersible pumps are numerous
- Efficiency Since they are submerged, these pumps do not require priming, and they can efficiently push water to the surface without losing pressure.
- Space-Saving Design Submersible pumps have a compact design, allowing them to fit into confined spaces, such as wells or basements.
- Reduced Noise Operating underwater significantly reduces noise levels, making them suitable for residential areas.
- Protection from Environmental Factors The sealed design protects the motor and components from corrosive substances and external elements, extending the life of the pump.
Conclusion
Submersible pumps are vital in various sectors, from agriculture to industrial applications. Their ability to efficiently pump fluids while submerged makes them indispensable tools for managing water resources and wastewater. As technology advances, the efficiency and functionality of submersible pumps continue to improve, ensuring their relevance in an ever-evolving landscape of fluid management.
-
Your Guide to Deep Well Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Why Choose a Stainless Steel Deep Well Pump?
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Understanding Water-Filled Submersible Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Understanding SS Submersible Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Reliable Submersible Well Pumps for Your Water Supply Needs
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Choosing the Right Submersible Pump for Your Water Management Needs
NewsOct.31,2024
-
 Understanding Water-Filled Submersible PumpsWhen it comes to selecting the right pump for your water management needs, understanding the different types available is crucial.Detail
Understanding Water-Filled Submersible PumpsWhen it comes to selecting the right pump for your water management needs, understanding the different types available is crucial.Detail -
 Guide to Installing a Deep Well Submersible PumpWhen dealing with deep wells, a deep well submersible pump is often the most effective solution for extracting water from significant depths.Detail
Guide to Installing a Deep Well Submersible PumpWhen dealing with deep wells, a deep well submersible pump is often the most effective solution for extracting water from significant depths.Detail -
 Finding the Right Submersible PumpWhen seeking an efficient solution for pumping water from deep wells, sumps, or other applications, the submersible pump is a leading choice.Detail
Finding the Right Submersible PumpWhen seeking an efficient solution for pumping water from deep wells, sumps, or other applications, the submersible pump is a leading choice.Detail
