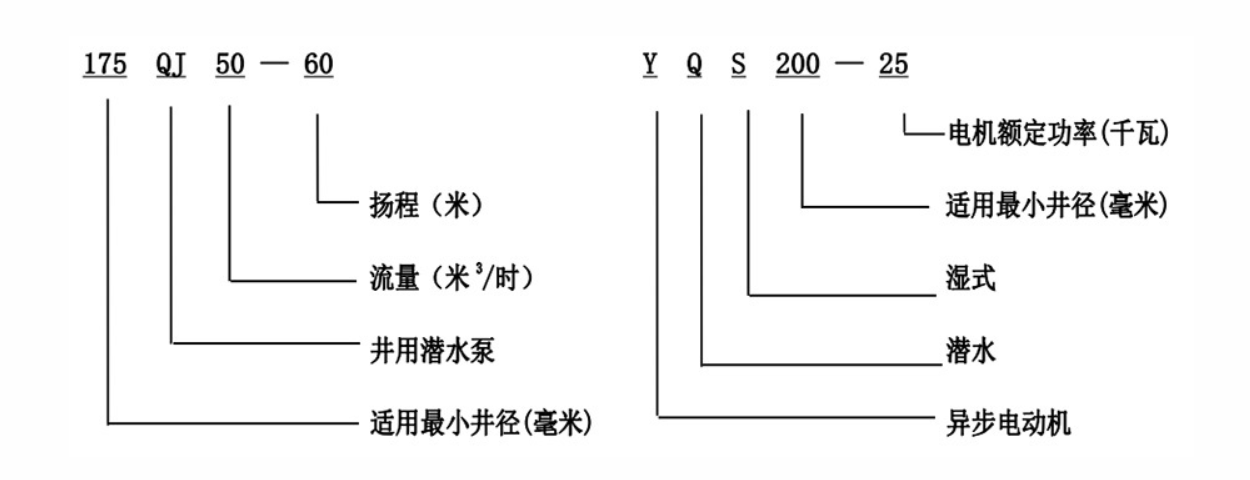
10 月 . 21, 2024 20:30 Back to list
Water-Filled vs Oil-Filled Submersible Pumps Key Differences and Benefits
Submersible Pump Water-Filled vs. Oil-Filled
Submersible pumps are essential devices used for a variety of applications, including draining water from basements, wells, and construction sites. They are designed to operate underwater, allowing them to efficiently move water or other liquids. One critical aspect in the design and operation of submersible pumps is the choice between water-filled and oil-filled models. This article explores the differences, advantages, and disadvantages of each type, helping users make informed decisions based on their specific needs.
Water-Filled Submersible Pumps
Water-filled submersible pumps, as the name suggests, utilize water as the primary coolant and lubricant within the motor. These pumps are typically designed for applications where the pump is fully submerged in water. Their main advantage is simplicity; they usually have fewer parts and a less complicated design compared to oil-filled versions. This simplicity often translates into lower costs and easier maintenance.
From an environmental perspective, water-filled pumps are generally more eco-friendly. Since they do not contain oil, there is no risk of oil leaks contaminating surrounding water sources. Additionally, users may find water-filled pumps suitable for potable water applications, as they do not use any substances that might compromise water quality.
However, water-filled pumps do have some limitations. They can often struggle in applications involving high temperatures or extreme conditions, as the water used for cooling can become less effective. Furthermore, these pumps may not perform as efficiently under high pressure, which could be a concern for some industrial applications.
Oil-Filled Submersible Pumps
submersible pump water filled vs oil filled
In contrast, oil-filled submersible pumps are filled with oil to cool and lubricate the motor. The oil used in these pumps can effectively manage heat, allowing them to operate at higher temperatures and in more demanding applications. This makes them suitable for environments like sewage or wastewater treatment, where the pump needs to handle heavy-duty tasks.
One of the notable benefits of oil-filled pumps is their ability to operate in deeper waters. The density of oil provides better buoyancy, which enhances the overall efficiency of the pump. Furthermore, oil helps reduce the wear and tear on mechanical components, potentially extending the lifespan of the pump.
However, oil-filled pumps are not without their drawbacks. The use of oil raises environmental concerns, as leaks can lead to contamination of water sources. Maintenance can also be more complex due to the need to monitor oil levels and replace the oil periodically. Additionally, if an oil-filled pump fails, it may result in significant environmental damage, leading to costly cleanup efforts.
Choosing the Right Pump
When deciding between a water-filled and oil-filled submersible pump, several factors should be considered. For general domestic tasks such as draining a pool or basement, a water-filled pump might be the ideal choice due to its cost-effectiveness and environmental advantages. However, for industrial applications requiring deeper submersion, higher temperatures, or larger volumes, an oil-filled pump may be necessary.
In conclusion, both water-filled and oil-filled submersible pumps have their respective benefits and drawbacks. Understanding the specific application and environmental factors is crucial when selecting the appropriate type of pump. By weighing these considerations, users can make choices that not only meet their operational needs but also adhere to environmental standards, ensuring efficient and responsible usage of these vital devices.
-
Your Guide to Deep Well Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Why Choose a Stainless Steel Deep Well Pump?
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Understanding Water-Filled Submersible Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Understanding SS Submersible Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Reliable Submersible Well Pumps for Your Water Supply Needs
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Choosing the Right Submersible Pump for Your Water Management Needs
NewsOct.31,2024
-
 Understanding Water-Filled Submersible PumpsWhen it comes to selecting the right pump for your water management needs, understanding the different types available is crucial.Detail
Understanding Water-Filled Submersible PumpsWhen it comes to selecting the right pump for your water management needs, understanding the different types available is crucial.Detail -
 Guide to Installing a Deep Well Submersible PumpWhen dealing with deep wells, a deep well submersible pump is often the most effective solution for extracting water from significant depths.Detail
Guide to Installing a Deep Well Submersible PumpWhen dealing with deep wells, a deep well submersible pump is often the most effective solution for extracting water from significant depths.Detail -
 Finding the Right Submersible PumpWhen seeking an efficient solution for pumping water from deep wells, sumps, or other applications, the submersible pump is a leading choice.Detail
Finding the Right Submersible PumpWhen seeking an efficient solution for pumping water from deep wells, sumps, or other applications, the submersible pump is a leading choice.Detail
