2 月 . 11, 2025 09:10 Back to list
water filled vs oil filled submersible pump
Choosing between water-filled and oil-filled submersible pumps requires a deep understanding of their design, function, and application. Each type has distinct advantages and situations they are best suited for, making an informed decision crucial for optimal performance and longevity.
When comparing these two types of pumps, it's essential to consider the specific needs of the application. For situations where clean water, environmental safety, and minimal maintenance are priorities, water-filled pumps are often the superior choice. This includes domestic water supply, irrigation systems, and certain commercial applications where contamination could have severe consequences. Conversely, for applications that demand high performance, greater durability, and can adhere to stringent maintenance schedules, oil-filled pumps might be more appropriate. These pumps excel in industries like mining, oil extraction, and wastewater management, where operational demands are high, and the risk of environmental contamination is minimized through controlled measures. Beyond their basic functions, advancements in technology are continuously enhancing the capabilities of both water-filled and oil-filled pumps. Variable frequency drives (VFDs) can be integrated with these pumps to optimize their efficiency, providing further customization to meet the unique demands of different applications. Additionally, smart technology now enables real-time monitoring and control, ensuring that pumps operate within their optimal parameters, thereby reducing wear and unnecessary energy consumption. In conclusion, choosing between water-filled and oil-filled submersible pumps involves analyzing the specific requirements of the application, considering environmental impact, maintenance capabilities, and cost-effectiveness. By carefully evaluating these factors, users can select a pump type that not only meets their immediate needs but also supports sustainable and efficient operation in the long term. Whether prioritizing eco-friendliness or durability, the right choice will enhance operational efficiency and reliability, establishing a foundation of trust and credibility with stakeholders.

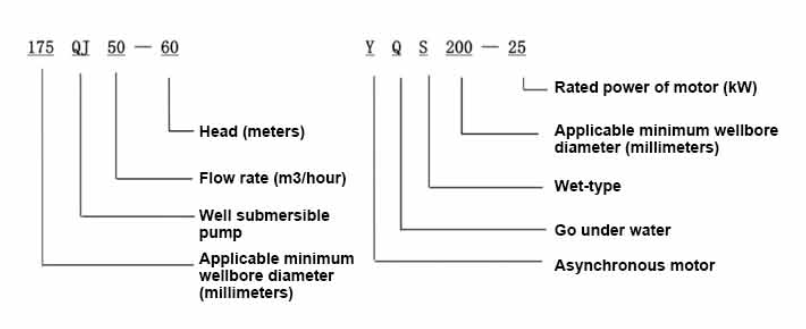
When comparing these two types of pumps, it's essential to consider the specific needs of the application. For situations where clean water, environmental safety, and minimal maintenance are priorities, water-filled pumps are often the superior choice. This includes domestic water supply, irrigation systems, and certain commercial applications where contamination could have severe consequences. Conversely, for applications that demand high performance, greater durability, and can adhere to stringent maintenance schedules, oil-filled pumps might be more appropriate. These pumps excel in industries like mining, oil extraction, and wastewater management, where operational demands are high, and the risk of environmental contamination is minimized through controlled measures. Beyond their basic functions, advancements in technology are continuously enhancing the capabilities of both water-filled and oil-filled pumps. Variable frequency drives (VFDs) can be integrated with these pumps to optimize their efficiency, providing further customization to meet the unique demands of different applications. Additionally, smart technology now enables real-time monitoring and control, ensuring that pumps operate within their optimal parameters, thereby reducing wear and unnecessary energy consumption. In conclusion, choosing between water-filled and oil-filled submersible pumps involves analyzing the specific requirements of the application, considering environmental impact, maintenance capabilities, and cost-effectiveness. By carefully evaluating these factors, users can select a pump type that not only meets their immediate needs but also supports sustainable and efficient operation in the long term. Whether prioritizing eco-friendliness or durability, the right choice will enhance operational efficiency and reliability, establishing a foundation of trust and credibility with stakeholders.
Latest news
-
Your Guide to Deep Well Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Why Choose a Stainless Steel Deep Well Pump?
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Understanding Water-Filled Submersible Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Understanding SS Submersible Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Reliable Submersible Well Pumps for Your Water Supply Needs
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Choosing the Right Submersible Pump for Your Water Management Needs
NewsOct.31,2024
-
 Understanding Water-Filled Submersible PumpsWhen it comes to selecting the right pump for your water management needs, understanding the different types available is crucial.Detail
Understanding Water-Filled Submersible PumpsWhen it comes to selecting the right pump for your water management needs, understanding the different types available is crucial.Detail -
 Guide to Installing a Deep Well Submersible PumpWhen dealing with deep wells, a deep well submersible pump is often the most effective solution for extracting water from significant depths.Detail
Guide to Installing a Deep Well Submersible PumpWhen dealing with deep wells, a deep well submersible pump is often the most effective solution for extracting water from significant depths.Detail -
 Finding the Right Submersible PumpWhen seeking an efficient solution for pumping water from deep wells, sumps, or other applications, the submersible pump is a leading choice.Detail
Finding the Right Submersible PumpWhen seeking an efficient solution for pumping water from deep wells, sumps, or other applications, the submersible pump is a leading choice.Detail
