2 月 . 15, 2025 19:15 Back to list
submersible pump cord
In the intricate arena of modern water management solutions, the submersible pump cord plays a pivotal role that deserves careful consideration. As the silent workhorse of submersible pumps, the cord must be intricately designed to ensure optimal performance, safety, and longevity of the entire system. Grasping the importance of a well-designed submersible pump cord is crucial for any professional working in water management, engineering, or related fields.
Maintenance plays a paramount role in extending the life of submersible pump cords. Regular inspections for wear and tear, along with scheduled replacements, can prevent unexpected failures. Experienced engineers recommend a routine check for signs of cracking, brittleness, or corrosion, particularly at the endpoints where most stress occurs. A reliable maintenance schedule is a testament to a well-managed water system, ensuring not only functionality but also safety for all involved. Establishing trust in these systems begins with a proactive approach to upkeep, honored by both engineers and end-users alike. Finally, the future of submersible pump cords is marked by advancements in technology. Innovations such as integrated sensors and smart technologies offer real-time data on cord health, providing an added layer of security and efficiency. Industry leaders are actively exploring these technologies to enhance predictive maintenance capabilities, reducing downtime, and fostering proactive management of water resources. The adaptability of professionals to these changes will define the next generation of water management solutions. In conclusion, the submersible pump cord is far more than a mere accessory; it is a critical component necessitating specialized knowledge and a commitment to quality. By prioritizing material integrity, electrical compatibility, and strategic maintenance, professionals can ensure the longevity and reliability of their water management systems. As technological strides continue to revolutionize this field, staying informed and adaptable remains the cornerstone of expertise and authority in managing submersible pump systems.
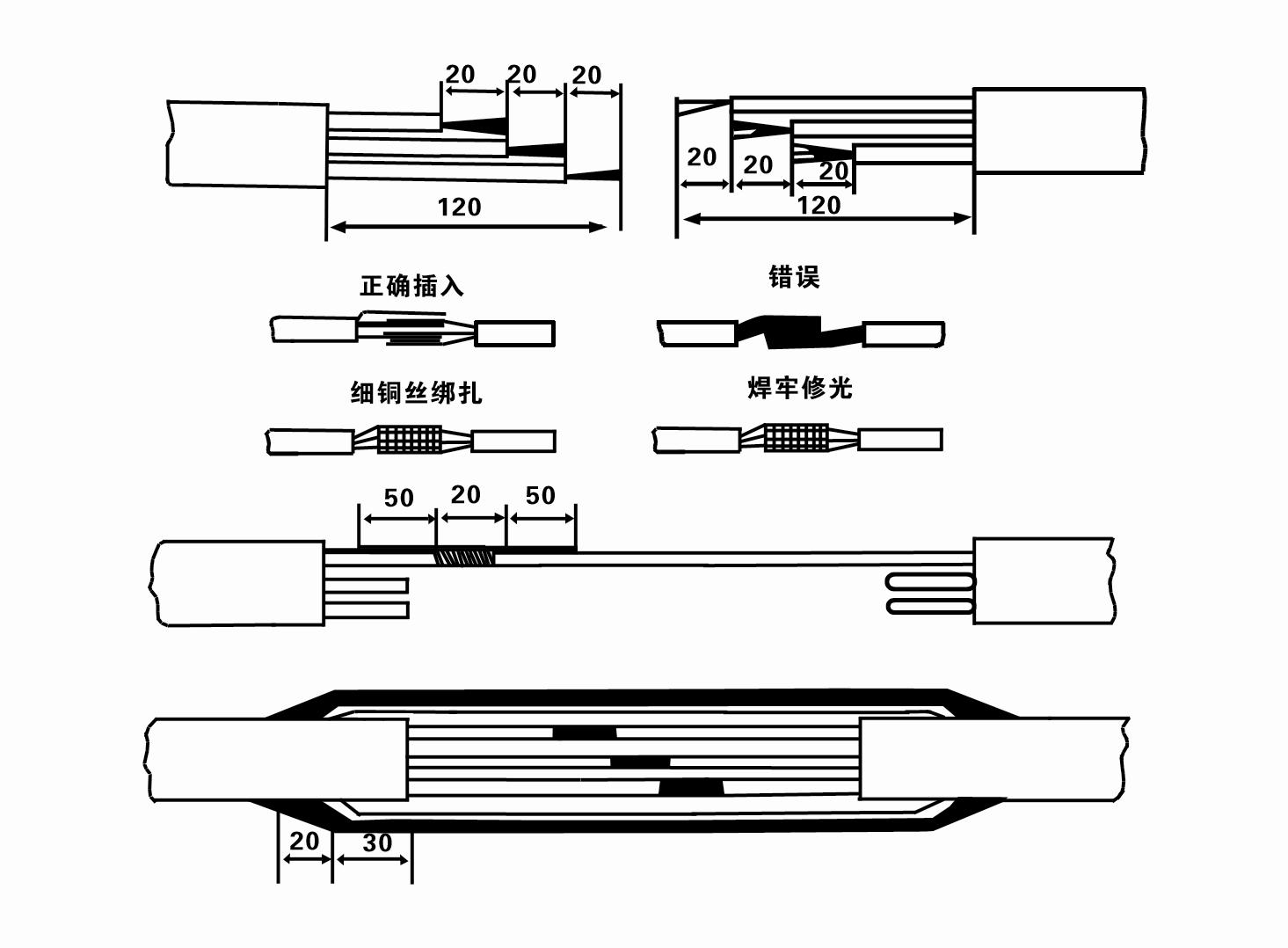

Maintenance plays a paramount role in extending the life of submersible pump cords. Regular inspections for wear and tear, along with scheduled replacements, can prevent unexpected failures. Experienced engineers recommend a routine check for signs of cracking, brittleness, or corrosion, particularly at the endpoints where most stress occurs. A reliable maintenance schedule is a testament to a well-managed water system, ensuring not only functionality but also safety for all involved. Establishing trust in these systems begins with a proactive approach to upkeep, honored by both engineers and end-users alike. Finally, the future of submersible pump cords is marked by advancements in technology. Innovations such as integrated sensors and smart technologies offer real-time data on cord health, providing an added layer of security and efficiency. Industry leaders are actively exploring these technologies to enhance predictive maintenance capabilities, reducing downtime, and fostering proactive management of water resources. The adaptability of professionals to these changes will define the next generation of water management solutions. In conclusion, the submersible pump cord is far more than a mere accessory; it is a critical component necessitating specialized knowledge and a commitment to quality. By prioritizing material integrity, electrical compatibility, and strategic maintenance, professionals can ensure the longevity and reliability of their water management systems. As technological strides continue to revolutionize this field, staying informed and adaptable remains the cornerstone of expertise and authority in managing submersible pump systems.
Next:
Latest news
-
Your Guide to Deep Well Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Why Choose a Stainless Steel Deep Well Pump?
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Understanding Water-Filled Submersible Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Understanding SS Submersible Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Reliable Submersible Well Pumps for Your Water Supply Needs
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Choosing the Right Submersible Pump for Your Water Management Needs
NewsOct.31,2024
-
 Understanding Water-Filled Submersible PumpsWhen it comes to selecting the right pump for your water management needs, understanding the different types available is crucial.Detail
Understanding Water-Filled Submersible PumpsWhen it comes to selecting the right pump for your water management needs, understanding the different types available is crucial.Detail -
 Guide to Installing a Deep Well Submersible PumpWhen dealing with deep wells, a deep well submersible pump is often the most effective solution for extracting water from significant depths.Detail
Guide to Installing a Deep Well Submersible PumpWhen dealing with deep wells, a deep well submersible pump is often the most effective solution for extracting water from significant depths.Detail -
 Finding the Right Submersible PumpWhen seeking an efficient solution for pumping water from deep wells, sumps, or other applications, the submersible pump is a leading choice.Detail
Finding the Right Submersible PumpWhen seeking an efficient solution for pumping water from deep wells, sumps, or other applications, the submersible pump is a leading choice.Detail
