2 月 . 11, 2025 08:34 Back to list
which is better oil filled or water filled submersible pump
When it comes to choosing between oil-filled and water-filled submersible pumps, the decision should be informed by an understanding of their distinct characteristics, advantages, and appropriate applications. Both types of pumps are designed for submersion in liquids, but they cater to different operational needs and environments.
Conversely, the maintenance requirements for water-filled pumps are generally lower, which can be advantageous for users seeking minimal intervention post-installation. The absence of oil also eliminates the need for oil level checks and replacement, making water-filled pumps an attractive option for applications where ease of maintenance is a priority. When evaluating which type of pump is better, it's crucial to consider the specific requirements of your intended application. If the application involves environments where oil leaks could pose a serious hazard or violation of regulations, water-filled pumps might be the preferable choice. These pumps align well with strict environmental standards and offer significant savings in terms of ongoing maintenance. In contrast, if the application demands robustness and the ability to perform under high stress conditions, an oil-filled pump may provide the required performance levels. Industries such as mining, construction, and heavy manufacturing often opt for oil-filled pumps due to their resilience and higher operational efficiency in difficult conditions. Ultimately, the choice between oil-filled and water-filled submersible pumps depends on a careful analysis of application-specific considerations, including environmental impact, maintenance capabilities, operational efficiency, and regulatory compliance. By weighing these factors, you can select a pump that not only meets your immediate needs but also offers long-term benefits in terms of performance and sustainability.
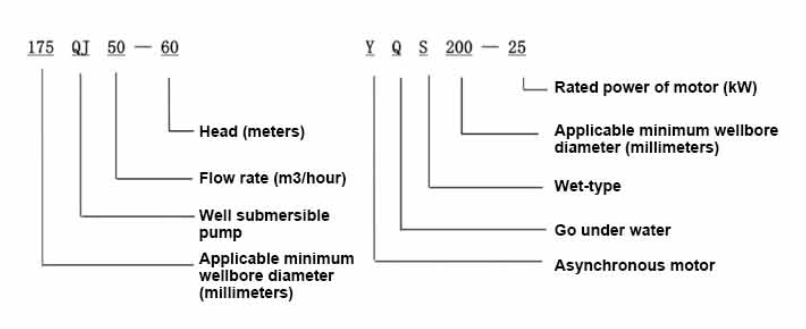
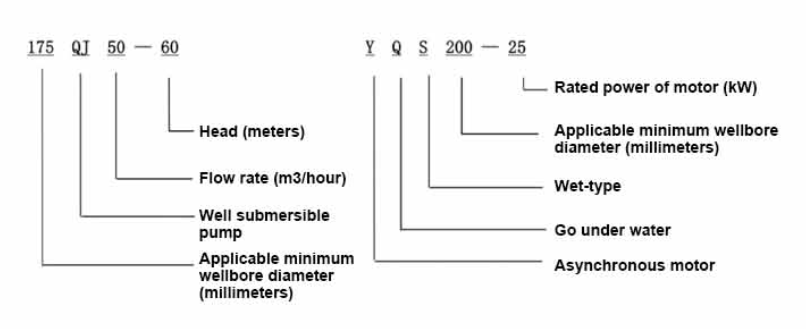
Conversely, the maintenance requirements for water-filled pumps are generally lower, which can be advantageous for users seeking minimal intervention post-installation. The absence of oil also eliminates the need for oil level checks and replacement, making water-filled pumps an attractive option for applications where ease of maintenance is a priority. When evaluating which type of pump is better, it's crucial to consider the specific requirements of your intended application. If the application involves environments where oil leaks could pose a serious hazard or violation of regulations, water-filled pumps might be the preferable choice. These pumps align well with strict environmental standards and offer significant savings in terms of ongoing maintenance. In contrast, if the application demands robustness and the ability to perform under high stress conditions, an oil-filled pump may provide the required performance levels. Industries such as mining, construction, and heavy manufacturing often opt for oil-filled pumps due to their resilience and higher operational efficiency in difficult conditions. Ultimately, the choice between oil-filled and water-filled submersible pumps depends on a careful analysis of application-specific considerations, including environmental impact, maintenance capabilities, operational efficiency, and regulatory compliance. By weighing these factors, you can select a pump that not only meets your immediate needs but also offers long-term benefits in terms of performance and sustainability.
Latest news
-
Your Guide to Deep Well Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Why Choose a Stainless Steel Deep Well Pump?
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Understanding Water-Filled Submersible Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Understanding SS Submersible Pumps
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Reliable Submersible Well Pumps for Your Water Supply Needs
NewsOct.31,2024
-
Choosing the Right Submersible Pump for Your Water Management Needs
NewsOct.31,2024
-
 Understanding Water-Filled Submersible PumpsWhen it comes to selecting the right pump for your water management needs, understanding the different types available is crucial.Detail
Understanding Water-Filled Submersible PumpsWhen it comes to selecting the right pump for your water management needs, understanding the different types available is crucial.Detail -
 Guide to Installing a Deep Well Submersible PumpWhen dealing with deep wells, a deep well submersible pump is often the most effective solution for extracting water from significant depths.Detail
Guide to Installing a Deep Well Submersible PumpWhen dealing with deep wells, a deep well submersible pump is often the most effective solution for extracting water from significant depths.Detail -
 Finding the Right Submersible PumpWhen seeking an efficient solution for pumping water from deep wells, sumps, or other applications, the submersible pump is a leading choice.Detail
Finding the Right Submersible PumpWhen seeking an efficient solution for pumping water from deep wells, sumps, or other applications, the submersible pump is a leading choice.Detail
